-
EAAFP Foundation 2022-2023 Small Grant Fund Reporting Workshop
Discussing a Potential Global Impact of Domestic Migratory Waterbird Conservation Efforts ©EAAFP On January 31st, the Reporting Workshop of the EAAFP Foundation’s…
Continue reading -
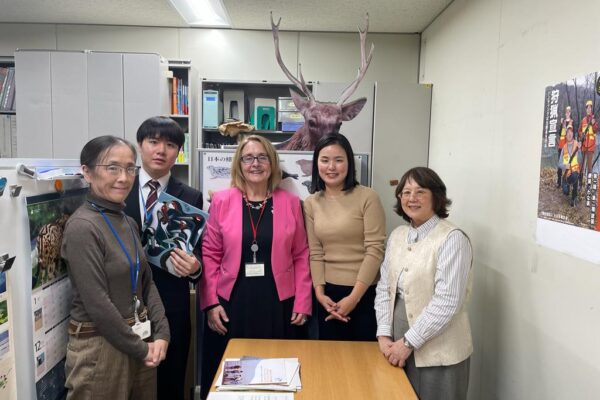
Japan Showcases National Partnership Strength at EAAFP Meeting
The East Asian–Australasian Flyway Partnership (EAAFP) Secretariat had the honour of witnessing the lively energy of Japan's National Partnership during a hybrid meeting held from December 7 to 10, 2023. This event held special significance for our Chief Executive, Jennifer George, who played a key role in crafting the EAAFP National Partnership Guidelines. Masterfully organised by BirdLife International Tokyo on behalf of the Japanese Ministry of the Environment, the gathering brought together a diverse audience, including high-level representatives from national and local governments, passionate NGOs, dedicated academics and researchers, and hardworking site managers and farmers who engaged in lively discussions and knowledge sharing. The meeting wasn't just about words; it was about experience. A pre-dawn visit to a designated Flyway Network Site offered a breathtaking spectacle—hundreds of geese erupting from the mist, ready for their daily forage. Later, a trip to a local rice farm shed light on the unique challenges and admirable efforts of those striving for both sustainable livelihoods and migratory waterbird conservation. Beyond sharing their own experiences, the Japanese participants generously extended their support to other national partners seeking to develop their own National Partnerships. The Secretariat stands ready to facilitate this knowledge exchange and provide any necessary assistance. The Japan National Partnership meeting wasn't just a gathering; it was a testament to the power of collaboration. It showcased the dedication of diverse stakeholders towards a shared goal—protecting the birds that bind us together across the flyway.
Continue reading -
Welcoming Paleik Lake (EAAF154) and Pyu Lake (EAAF155) as new Flyway Network Sites of Myanmar
Paleik Lake © Thiri Dae We Aung/BANCA Pyu Lake © Thiri Sandar Zaw On the 16th of November 2023, the East Asian-Australasian Partnership (EAAFP) welcomed the addition of two new Flyway Network Sites (FNS) of the Republic of the Union of Myanmar namely, Paleik Lake (EAAF154) and Pyu Lake (EAAF155), marking the seventh and eighth FNS in the country. Flock of Greylag Goose recorded in December 2016 at Paleik Lake FNS © Thiri Dae We Aung/BANCA Recognised as an Important Bird and Biodiversity Area (IBA) and a Key Biodiversity Area (KBA), Paleik Lake (EAAF154) provides food and shelter to globally threatened migratory waterbirds such as Critically Endangered Baer’s Pochard (Aythya baeri), Vulnerable Common Pochard (Aythya ferina), and other more abundant species including Greylag Goose (Anser anser), Glossy Ibis (Plegadis falcinellus), and Black-headed Ibis (Threskiornis melanocephalus), as well as a breeding ground for other waterbird species. Paleik Lake is also known to provide a variety of livelihood benefits to local communities primarily through agriculture and aquaculture by supplying water for the cultivation of rice and vegetables and as a habitat for economically important fishes and aquatic plants. Additionally, Paleik Lake plays a vital role in mitigating and adapting to climate change, specifically in preventing droughts and floods during extreme weather events. Diving duck species observed at the northeast part of Pyu Lake FNS in January 2019 © Thiri Dae We Aung Home to a diverse population of aquatic flora and fauna, Pyu Lake (EAAF155) annually supports up to 40 waterbird species including the Critically Endangered Baer’s Pochard (Aythya baeri) and the Vulnerable Common Pochard (Aythya ferina). Pyu Lake is characterised by its surrounding agricultural land with abundant crops that support the livelihoods of local communities. In addition, the presence of economically significant aquatic plants and fish in the lake greatly contributes to the preservation of traditional fishing practices among the local villagers. With no prior conservation frameworks in place or national/local legal recognition as a critical habitat for migratory waterbirds and other species, Pyu Lake’s designation as an FNS is a crucial step in ensuring that further biodiversity loss is minimised, and appropriate conservation measures are implemented. Myanmar’s Ministry of Natural Resources and Environmental Conservation established the Mandalay Region Wetlands Conservation Committee which enables the conduct of annual wintering survey and Asian Waterbird Census in both Paleik Lake and Pyu Lake, the implementation of education awareness activities focusing on migratory waterbird species, among others. Since 2016, the Biodiversity and Nature Conservation Association (BANCA) performs the annual waterbird monitoring in both sites. Moreover, the Paleik Bird Lover Association and Shwe Kan Tharyar Nature Conservation Association are local conservation groups established to conserve the biodiversity of Paleik Lake and Pyu Lake, respectively. With the valuable support of national and local conservation groups, the designation of Paleik Lake and Pyu Lake offers a ray of hope for enhanced governance and management of wetland ecosystems in Myanmar. As part of their conservation measures, management plans for Paleik Lake and Pyu Lake are intended to be developed. Both FNS are also recommended for designation as Ramsar sites by the Ramsar Administrative Authority of the Forest Department of Myanmar. The expansion of the Flyway Site Network exemplifies the unwavering commitment of the EAAFP and its Partners in conserving and restoring important habitats for migratory waterbirds both for nature and people. It is a truly remarkable partnership driven by our shared goals and appreciation to safeguard the connectivity of wetland habitats along the flyway, thereby providing safe havens for migratory waterbirds.
Continue reading -
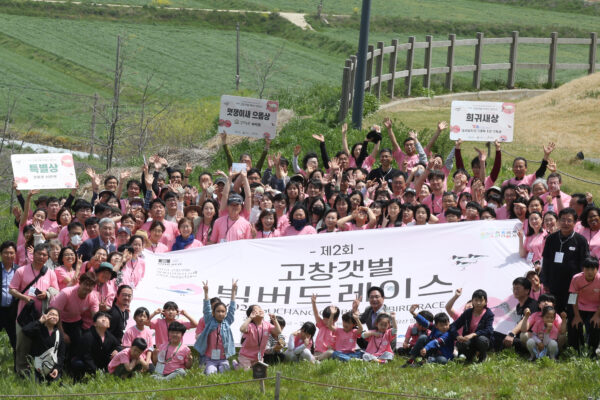
Gochang Big Bird Race 2023 brought birdwatchers to contribute bird data to the UNESCO World Heritage Site
From 21st to 23rd April 2023, the 2nd Gochang Big…
Continue reading -
Activities of the EAAFP Secretariat for Hwaseong Wetlands Conservation Projects 2020-2022
The scenery of the Hwaseong Wetlands Flyway Network Site © EAAFP Secretariat In November 2018, Hwaseong Wetlands was nominated as the East Asian-Australasian Flyway Network Site (FNS) as its importance as a habitat for migratory waterbirds has been acknowledged. With its designation, Hwaseong City and the EAAFP Secretariat signed an MOU [article] and proceeded with the project called “Collaboration for Conservation of the Hwaseong Wetlands” for three consecutive years, from 2020 to 2022. This article demonstrates the project activities that were carried out in chronological order. <2020> The Project was carried out in six major activities. EAAFP, Birds Korea, Federation for Environmental Movements of Hwaseong (KFEM Hwaseong), Korea Federation for Environmental Movements (KFEM), and Hwaseong City together prepared for the event from June, proceeding with the international symposium online in December 2020. About 300 concurrent users with 2400 views participated and discussed the management of Hwaseong Wetlands together with citizens, farmers, fishermen, the Rural Community Corporation, the Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries, the Ministry of Environment, researchers, international organizations, and overseas experts. Article: Link Follow-up Actions to the Symposium: Production of Guidelines for Hwaseong Wetland Management Plan and Workshops. Based on discussions on the management of Hwaseong Wetlands at the symposium in December 2020, the EAAFP Secretariat presented guidelines for Hwaseong Wetland Management Plan after two workshops and one advisory meeting in February and March 2021. Hwaseong City, Hwaseong Eco Foundation, and the Symposium Task Force team (the EAAFP Secretariat, KFEM, KFEM Hwaseong, and Birds Korea) participated in the workshop to reach an agreement on the direction of Hwaseong Wetland management in 2021 and beyond. The title of the guideline is ‘The Proposal for the Management Directions for the Sustainable use of the Hwaseong Wetlands’ and was referred to domestic and international wetland management plans and management guidelines. This suggestion presents the scope of management, direction of wetland management, partnership establishment, and setting of goals and implementations. It also proposes to form a consultative body when establishing a partnership, to have an implementation organization accordingly, and to entrust it to civic groups, which has not been attempted in Korea. The authors of the guidelines are Ms. Yeonah Ku (EAAFP Secretariat), (KFEM Hwaseong), and Ms. Hyeseon Do (EAAFP Secretariat), members of the Symposium TF. The external manuscript of Han Donguk, the Director of the PGA Wetland Ecology Research Institute, was also included. Article: Link Hwaseong Wetlands Conservation Resident Project The resident project organized by HEFM initially considered the formation of a symposium preparatory committee, but because of the rising number of COVID-19 cases, it was more carried out as an awareness-raising-oriented activity. From July 2020 to March 2021, six meetings, seven campaigns, eight club activities, two discussions, three lectures, five civic ecological research group activities, and one ecological exploration activity were held. Article: Link International Cooperation Project for the Conservation of Far Eastern Curlew The EAAFP Secretariat discussed with EAAFP Far Eastern Curlew Task Force and decided to support the “Far Eastern Curlew Conservation Project in Sumatra Island” and funded the EKSAI Foundation in Indonesia. Through this research, a full investigation of Far Eastern Curlew and waterbirds in northern Sumatra including Sembilang National Park (South Sumatra Province), Pantai Cemara (Jambi Province) and Bagan Serdang (North Sumatra Province) was made, and training was conducted to local guards. Moreover, a report that compares and analyzes with waterbirds data has been written, which is uploaded on the EAAFP website. Article: Link Waterbird-oriented Ecological Survey and Far Eastern Curlew Network Construction Project Organized by Birds Korea and KFEM, ecological surveys at the Hwaseong Wetlands were carried out from June 2020 to March 2021. Through the survey, migration behavior and habitat of migratory waterbirds and their juvenile were identified. Based on the findings, guideline directions were proposed, and the Far Eastern Curlew Network was formed in December 2020. Among the findings, a report written in 2020 is uploaded on the EAAFP website. Related article 1: “Flyway: connecting people and migratory waterbirds” story series #6– Interview with Dr. Nial Moores Related article 2: The Hwaseong Wetlands Project Related article 3: The Launch of Far Eastern Curlew Network of the Korean Peninsula Promotional and Educational Materials Production Project The EAAFP Secretariat produced key species factsheets for public-raise awareness purposes in the East-Asian Australasian Flyway. The nine species were produced in both Korean and English. Article: Link Moreover, EAAFP Secretariat operated Hwaseong Wetlands FNS Facebook from July 2020 and is promoting Hwaseong Wetlands conservation activities. Article: Link Furthermore, prizes for the Hwaseong Wetland Promotion Contest winner were delivered. [Prize-winner] <2021> The Project was carried out in four major activities. International Cooperation Project for the Conservation of Far Eastern Curlew Following the previous activity of the Far Eastern Curlew surveys in Sumatra in Indonesia, the EKSAI Foundation took another series of surveys as well as training local communities in Sumatra. See the results and the reports in the separate article: Link Local Cooperation Project: Far Eastern Curlew Network in the Korean Peninsula Following the suggestion from the EAAFP Secretariat and Birds Korea in 2020 based on the ecological survey in the Hwaseong Wetlands Flyway Network Site (FNS) in 2020 and existing data from the National Institute of Biological Resources (NIBR), three local governments in ROK, Hwaseong City, Seocheon County, Yeonsu District of Incheon City, initiated the Far Eastern Curlew Network in the Korean Peninsula since 1st December 2020. As a secretariat of the network, Hwaseong City supported the Far Eastern Curlew survey held in July 2021, following the advice of Birds Korea and the EAAFP Secretariat. From July 21st to 25th 2021, 26 survey participants counted Far Eastern Curlews and other species at 34 sites in three areas: parts of coastal Incheon (Ganghwa Island, Yeongjong Island and Songdo, the Han Estuary); the adjacent Gyeonggi Coast (the Hwaseong Wetlands and Asan Bay); and the Geum Estuary (Figure 1). Participants are experienced counters with specialist knowledge of their areas. A total of 9,642 Far Eastern Curlews were recorded with 3,746 in Incheon; 3,255 in parts of Gyeonggi mainland coast; and 2,641 in Geum Estuary. This is around a third of the world’s population of the species, which was estimated to be 32,000 individuals (range: 20,000 – 49,000 individuals, source: https://www.iucnredlist.org/) Article: Link Local Residents Support Project: Citizen Ecological Survey, Marine Waste Cleaning, Civic Forum, and Walking Event To promote the importance of the Hwaseong Wetlands and to conserve wetlands in the hands of the local people, the EAAFP Secretariat and the Korean Federation of Environmental Movement–Hwaseong (KFEM Hwaseong) implemented the Local Residents Project for Conservation of the Hwaseong Wetlands from April to December 2021. Through the Project a citizen-based ecological survey group was formed, and ecological surveys and on-site monitoring activities were conducted with the guide led by experts in waterbirds, large benthos, wild animals, and amphibians. The Youth at Durae Natural High School near the Hwaseong Wetlands and instructors working in the region formed a small group (Dingo Club) together and conducted 5 times of indoor and field education activities regarding the Hwseong Wetlands. The students participated in the “Hwaseong Youth Policy Proposal Contest” and proposed policies for establishing the “Hwaseong Wetland Education Center” and won the Excellence Award. A local birdwatching and marine waste cleaning events were also held for the local citizens, providing sufficient education regarding marine waste problems and the importance of waterbirds. Furthermore, A civic forum was held with wetland NGOs, experts, and residents, titled ‘Benefits of the Hwaseong Wetlands, Shared with Together.’ Through the Forum, it was an opportunity to resolve conflicts over wetland development & conservation, seek new directions for reclaimed land in the Hwaseong Wetlands, and emphasize the importance of the Hwaseong Wetlands in and outside Hwaseong City. Lastly, Hwaseong Wetland Citizens’ Walking Event: Life and Peace Road was organized in solidarity with 17 civil society organizations in Suwon and Hwaseong Cities. Walking along the 5km section of the Hwaseong seawall, citizens toured the Hwaseong Wetlands, where numerous lives are alive and breathing, and shared the meaning of peace by listening to the story of the village suffering from 54 years of combat airfield at Maehyang-ri History Hall. Article: Link 2021 International Symposium for the Hwaseong Wetlands – “All Connected through the Hwaseong Wetlands: One World, One Future” On 26th November, the 2021 International Symposium for the Hwaseong Wetlands hosted by Hwaseong City took place at Purmir Hotel, Hwaseong City. Hwaseong Eco Foundation, EAAFP Secretariat, Birds Korea, and Korea Federation for Environmental Movements (KFEM) of Hwaseong co-organized the event, with support from the Ministry of Environment Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries, Cultural Heritage Administration of the Republic of Korea, and Hanns Seidel Foundation Korea. Based on the ideas drawn from the forum, the speakers raised the management and restoration plan on Tidal Flats in ROK with a policy proposal and discussed how to join force for the UNESCO World Natural Heritage Site Phase II. In addition, international experts presented the importance of designating the inland wetlands along the Hwaseong Lake as a Wetland Protected Area and the future management guidelines of the Hwaseong Wetlands with moderation by, Ms. Choony Kim, Secretary General of KFEM. During the panel discussion, the panelists emphasized the importance of designating the inland wetlands along the Hwaseong Lake as a Wetland Protected Area and the future management guideline of the Hwaseong Wetlands. Article: Link Symposium Video Links: Korean, English <2022> The Project was carried out in four major activities. International Cooperation Project for the Conservation of Far Eastern Curlew & domestic cooperation The afterwork has been conducted for the Far Eastern Curlew Conservation Project in Sumatra, Indonesia from January and February. The report document was revised according to the updated information provided by the EKSAI Foundation, the leading organization of the Fare Eastern Curlew Conservation Project in Sumatra. FEC Survey has been conducted in the Philippines from October to December 2022. The surveys were conducted in Bulacan, Malolos City, Pamarawan; National Capital region, Navotas City, Tansa; Cebu, Mandaue City; Negros Island, Negros Occidental; Iloilo City, Iloilo Province; Masbate State, Bicol Region; Oriental Mindoro; and La Union. With this survey there was an opportunity to introduce potentially important habitats for FEC in the Philippines and share survey data. It was reported that further support is required for the continuous implementation of the survey. In the other hand, the Secretariat supported the Hwaeong Eco Foundation and Hwaseong City by holding several meetings/ participating in several education trainings as a domestic cooperation activity. Hwaseong Wetlands Visioning Project In consultation with Wildfowl and Wetlands Trust (WWT) Based in UK, Hwaseong City and the EAAFP Secretariat have discussed the need for developing a visioning plan for the wise use of the Hwaseong Wetlands, which could positively support both wildlife and local residents that rely on the wetland areas. From January 2022, virtual meetings between WWT and the EAAFP Secretariat were held to discuss WWT’s site visit and the organization of stakeholder meeting to receive comprehensive data on the Hwaseong Wetlands for the development of the visioning report. The WWT’s visit (4 days) to the Hwaseong wetlands were proceeded in May, accessed relevant information of the site and two local stakeholder meetings were organized to gather perceptions and advice to reflect on the visioning report. Furthermore, the EAAFP Secretariat provided supplementary data to support the drafting of the visioning report. The final drafts were made in early 2023. Article: Link Local Residents Support Project: Citizen Ecological Survey Training Following theory-based training provided by experts in March 2022, a citizen-based ecological survey group was formed, and ecological surveys and on-site monthly monitoring activities were conducted with the guide led by experts in waterbirds, large benthos, halophytes, wild animals, and amphibians, from March to November 2022. The Citizen Ecological Survey Workshop was held on 27~28 November 2022 to share the survey activities and discuss strengths, weaknesses, and future improvements for the project. Article: Link Prepared by Ms. Yeonah Ku (Local Project Coordinator) & Mr. Yong June Kim (Programme Assistant) from EAAFP Secretariat
Continue reading -
Japan and U.S.A. announced Sister Site Agreement to strengthen collaboration to conserve migratory waterbirds
On 8th February, 2023, the Government of Saga City, Japan and the Bureau of Land Management (BLM)-Alaska signed the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) establishing a Sister Site relationshipbetween Flyway Network Sites Higashiyoka-higata (EAAF 124) of Japan and Qupałuk (EAAF 133) of U.S.A. The agreement promotes closer collaboration on conserving migratory waterbirds. A virtual signing ceremony was held, with Mr. Hidetaka Sakai, Mayor of Saga City, and Mr. Steve Cohn, Alaska State Director, BLM signing the MoU. ©Saga City, Japan ©BLM Both Flyway Network Sites (FNSs) are important for migratory shorebirds, especially for Dunlin (Calidris alpine articola), which is the most abundant shorebirds in Japan, and Qupałuk is high quality nesting habitat. Under the EAAFP Flyway Site Network, the Sister Site Agreement encourages the two FNSs to cooperate in research and monitoring of species of common and their habitats, allow information exchange on conversation and habitat management. In addition, the agreement includes efforts on CEPA (Communication/Capacity Building, Education, Participation, and Awareness) activities to enhance exchange between the sites. Mr. Steven Cohn, State Director of BLM-Alaska expressed, "As managers of valuable nesting habitat, it is important for the BLM to collaborate with partners throughout the flyway to support holistic habitat management through the full life cycles of species. We look forward to this partnership with Saga City to coordinate on bird monitoring, habitat management, and education and outreach." Mr. Hidetaka Sakai, Mayor of Saga City, said, “I am delighted that we could establish this Sister Site partnership. The sites are not just essential for the migratory birds, but for our livelihoods as well, and in order to conserve them, it is necessary to have initiatives that go beyond borders. Through this sister site partnership, we will encourage people to think and act on a global scale regarding their conservation and sustainable use. I have high hopes that our efforts will lead to a prosperous future.” Dr. Keiichi Nakazawa, Director of Wildlife Division, Nature Conservation Bureau, Ministry of the Environment, Japan emphasized, “Higashiyoka-higata became the 33rd Flyway Network Site in Japan in 2016, and it is one of Japan's most prominent migratory stopover and wintering sites for waterbirds, including endangered species such as Saunders’s gull, Black-faced spoonbill, and Common shelduck; making a treasure trove of biodiversity. We are very pleased that Qupałuk and Higashiyoka-higata have concluded the Sister Site Agreement under the EAAFP, and we would also like to express our sincere respect for the conservation efforts made to date. Our ministry will continue to support initiatives conducted for the migratory waterbird conservation between the two wetlands.” Qupałuk is located in the northeast of Teshekpuk Lake in the northeast corner of the National Petroleum Reserve in Alaska on the Arctic Coastal Plain in Alaska, U.S.A. The site covers over 21,000 hectares of near-pristine tundra, wetland, and open water habitat. Qupałuk hosts approximately 30,000 total nesting migratory birds and is an important habitat for molting geese and eiders. The site is home to a high density of nesting Dunlin, with an estimated population of 6,000. It is the second Flyway Network Site in the U.S.A and is the first managed by the Bureau of Land Management-Alaska. To the Iñupiat people, the Alasak Natives who have lived harmoniously on this land for millenia, Qupałuk means “small shorebird”. Qupałuk © Kiliii Yuyan Located on the northern shore of the Ariake Sea in Japan, Higashiyoka-higata has the largest remaining area of tidal flats in the country. The 218-hectare mudflat regularly supports 1% of the flyway population of Endangered Black-faced Spoonbill and Vulnerable Saunders’s Gull, and more than 10,000 migratory waterbirds visit the site annually. Higashiyoka-higata was also designated as a Ramsar Site in 2015. The area used to be called Daijugarami and the traditional knowledge, techniques and food culture were retained and passed on for many generations. Higashiyoka-higata © Saga City, Japan The EAAFP Flyway Site Network was established to ensure a network of internationally important sites is sustainably managed to support the long-term survival of migratory waterbirds within the EAAF. To date, there are 152 Flyway Network Sites in EAAF. Under this network, the EAAFP Sister Site agreement offers a mechanism for Flyway Network Sites to collaborate closely on monitoring and research, capacity-building, sharing and exchanging information and experiences, and CEPA activities. Guidelines for the EAAFP Sister Site Program will be adopted during MOP11. More information Flyway Site Network: https://www.eaaflyway.net/the-flyway/flyway-site-network/ Sister Site Programme: https://www.eaaflyway.net/sister-sites/ Further reading https://alaskausfws.medium.com/a-little-birds-big-sisters-e071dfe57eac
Continue reading -
Updates of HPAI recorded in East Asian – Australasian Flyway
Since November 2021, a series of unprecedent outbreaks of HPAI (Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza) occurred in western Eurasia and depleted significant percentages of waterbirds and seabird populations: Barnacle Goose in Scotland, Eurasian Crane in Israel, Dalmatian Pelican in southeastern Balkans and seabirds along the coast of the Atlantic Ocean. However, no significant incidents were reported from the East Asian-Australasian Flyway except die-offs of several hundred seabirds, such as Tufted Puffins and Rhinoceros Auklets, recorded around the waters of Kunashir Islands in southern Kuril in August 2022, which no official evidence of an HPAI outbreak was indicated by the time of writing. Yet, outbreaks of HPAI was recorded in cranes and other migratory waterbirds in the EAA Flyway in recent two months. Hooded Cranes in Suncheon Bay © Suncheon City On 1 November 2022, a Hooded Crane was found dead at Izumi, Japan and about one week later it was confirmed to be HPAI positive. Numbers of dead birds escalated since, reaching a daily peak of 74 dead Hooded Cranes collected on 17 November. Dead White-naped Cranes were recorded starting on 14 November. The number of daily totals of dead cranes decreased to less than 15 carcasses found from 8 December. As of 23 December 2022, the total number of carcasses of Hooded Cranes collected at Izumi were at least 1,097 and White-naped Crane at least 47. Three Hooded Crane carcasses testing positive of HPAI were collected from Kyushu: 2 from Isahaya and 1 from Akune (Information from the website of Ministry of the Environment Japan, link). Movements of cranes departing from Izumi, Japan were observed from late November. At the same time, there was a surge in the number of Hooded Cranes wintering at Suncheon, Ro Korea. It was speculated some cranes moved from Izumi to wintering sites in Ro Korea. This was proven by Hooded Cranes tracked by Dr Li Xianda in China (from Izumi, Japan to Chonsu Bay, Ro Korea in late November 2022). However, such movement is not irregular as Dr Li’s tagged Hooded Cranes were also recorded travelling between wintering sites in Japan and Ro Korea in 2020 and 2021 (Per. comm. from Li Xianda to Simba Chan). The number of Hooded Cranes at Suncheon reached a peak of several thousand birds in late November but started to decrease to about 3,500 birds in early December. It is believed cranes moved to Chonsu Bay and Galsa Bay, other wintering sites of Hooded Cranes in Ro Korea. The first dead Hooded Crane was found at Suncheon on 13 November. As of 12 December, 158 dead Hooded Cranes and one dead White-naped Crane were found in Ro Korea. On 20 November one sick Red-crowned Crane was captured in Kushiro, Japan and it was tested HPAI positive one week later. However, this should be seen as an independent case of HPAI from the wintering grounds in western Japan. In response to the HPAI outbreak, the Crane Working Group of the EAAFP held an emergency zoom meeting on 12 December and a proposal for reactions to the HPAI in the EAAF region was submitted to the EAAFP Secretariat. The Crane Working Group also sent warnings to other crane wintering sites. So far no abnormal crane deaths has been reported from China and the wintering sites were advised not to artificially feed cranes to avoid concentrations of cranes and other wintering birds. The Crane Working Group has also contacted crane researchers in Israel on possible links between the present incident and the HPAI outbreak at Hula Valley in December 2021, in which about 8,000 Eurasian Cranes died. Advice from Israeli colleagues was to remove crane carcasses especially those in water as quickly as possible and also avoid artificial feeding that would result in concentration of birds. In late November to early December, 34 dead Oriental Storks were found near Tianjin, at the coast of Bohai, China. Poisoning from poachers and HPAI have been ruled out and the cause of death is still under investigation. On 24 November and 12 December, dead Black-faced Spoonbills were found at Mai Po Nature Reserve and Hong Kong Wetland Park in Hong Kong S.A.R. respectively, were confirmed to be HPAI positive. On 9 December another dead Black-faced Spoonbill collected at Kumamoto Prefecture, Japan was also found to be HPAI positive. It is speculated more birds may have died during migration but were not found or reported. At the time when this news release was written, catastrophic HPAI outbreaks are occurring in Latin America, particularly along the coast of Peru where more than 20,000 dead seabirds (majority Peruvian Pelicans) recorded. The massive outbreaks of HPAI that started in western Eurasia in late 2021 are now being recorded in the East Asian Australasian Flyway. The Crane Working Group contacted other species working groups and task forces and almost all agreed on actions that should be taken as soon as possible. While we proposed strategies to be discussed at meetings in 2023, we also urge managers and local stakeholders at important waterbird/seabird sites to take precautions as suggested below, and countries along the flyway should keep in close communication on new cases of outbreaks. Recommendation to important waterbird/seabird sites: Have at least one staff member in charge of biosecurity. Have a contingency plan following the guidance of national authorities in case of outbreak of avian influenza and other avian diseases. Ideally the plan will be rehearsed every year before migratory seasons so staff and volunteers of the site understand all procedures and their roles in case of emergency. Have a contact list of agencies and institutions that can provide support during an outbreak. Have regular monitoring and surveillance on wild birds, particularly when outbreaks are reported along the flyway. In case sick and/or dead birds are found, try to collect them without causing disturbance to other birds. Although the risk of HPAI transmitting to human is low, personal protective equipment has to be used when handling sick or dead birds and the methods of collection and handling should follow national guidelines. Photographing the dead bird for records and to identify the species and gender. Useful references: 2007. Wild Birds and Avian Influenza: an introduction to applied field research and disease sampling techniques. Edited by D. Whitworth, S.H. Newman, T. Mundkur and P. Harris. FAO Animal Production and Health Manual, No. 5. Rome. (download from here) CMS Scientific Task Force on Avian Influenza and Wild Birds Issues Recommendations (2022) (visit the webpage here). Hacen Mohamed El-Hacen. 2022. Workshop report: Development and consequences of the recent bird flu outbreak among Sandwich terns in the Wadden Sea and adjacent areas (download from here) Scientific Task Force on Avian Influenza and Wild Birds statement on: H5N1 Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza in poultry and wild birds: Winter of 2021/2022 with focus on mass mortality of wild birds in UK and Israel (2022) (download from here) Wildlife Health Australia (2021) The sixth issue Wild Bird News June 2021 - National Avian Influenza Wild Bird Surveillance Newsletter (download from here) More references and useful links are available on webpage of Avian Influenza Working Group (link), News links: Ministry of the Environment, Japan: 高病原性鳥インフルエンザに関する情報 | 自然環境・生物多様性 | 環境省 (env.go.jp) News about dead seabirds washed to Kunashir Islands in southern Kuril (available on 12 August, 2022, visit the webpage here) Article prepared by Crane Working Group.
Continue reading -
Not just funding but also capacity-building opportunities! Asian Waterbird Conservation Fund (AWCF) is now receiving new applications!
The AWCF was established by WWF-Hong Kong in July 2005 to provide financial support for projects at sites of importance for migratory…
Continue reading -
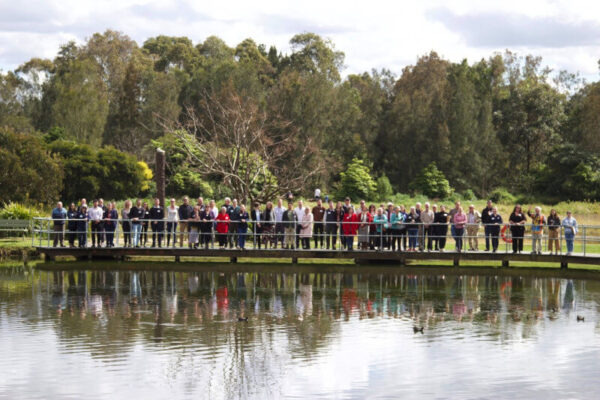
The Hunter Estuary Forum 2022
0 Participants of Hunter Estuary Forum ©Hunter Wetlands Centre The Hunter Estuary in Newcastle NSW, Australia is a place of great contrasts. It hosts the most important estuary in NSW for migratory shorebirds, the Hunter Estuary National Park and the Hunter Estuary Ramsar site, which includes Hunter Wetland Centre, Australia’s first dedicated wetlands centre. The Hunter Estuary is also home to the largest export facilities for both thermal and manufacturing coal in the Southern Hemisphere. Since the early 1980’s the Hunter Estuary has benefitted from four significant wetland restoration projects, beginning with the restoration of a small area of drained and degraded wetlands which was to become Hunter Wetlands Centre. Each of these restoration projects took lessons from what had gone before. Most importantly strong social partnerships among community conservation organisations, governments and industry organisations underpinned these achievements. Earlier this year Hunter Wetlands Centre proposed the idea for a Hunter Estuary Forum to commemorate the 20th anniversary Hunter Wetlands Centre being listed as a Ramsar site and to open a conversation among estuary stakeholders that have a role as managers, knowledge holders, service providers and educators for the estuary. Such an event would provide the opportunity to reconnect with our shared conservation history The forum program was designed in partnership with Australian Ramsar Administrative Authority (Federal Department of Climate Change, Energy, Environment and Water), NSW National Parks and Wildlife Service and Hunter Bird Observers Club. EAAFP also came on board in recognition of the Hunter Estuary as Site Number 10 on the East-Asian Australasian Flyway Site Network. On 31 August, participants from Local Government, State Government, Industry groups and non-government conservation organisations joined together at Hunter Wetlands Centre to hear from both keynote speakers and estuary locals from many sectors on the priorities and the challenges for the Hunter Estuary. The response to the event and the engagement on the day was very encouraging. It was clear from discussions from the floor and in break-out groups that collaboration across sectors has been a missing ingredient in recent years. There was strong concensus among participants on the need for a collaboration mechanism that could provide a neutral space where shared objectives might be developed. The Hunter Estuary and surrounding catchment has a unique opportunity to demonstrate a collaborative and cooperative approach to conservation and management of our coastal environment. We have the opportunity to leverage the science and knowledge underpinning the Hunter Estuary to guide coastal wetland restoration and identify transferrable learnings that can be used in other coastal communities. There was strong support for continuing the Hunter Estuary Forum process where some of these threads can be developed and it is hoped that a follow-up event can be held by mid 2023. Through sharing knowledge and experience, we may be better able to consider innovative management models that can deliver mutual benefits for our estuary and its stakeholders. Article prepared by: Christine Prietto, HWCA Ramsar Officer, Hunter Estuary Forum Convenor, Ramsar NGO CEPA Focal Point, Australia Official website of Hunter Estuary Forum: https://wetlands.org.au/hef/
Continue reading