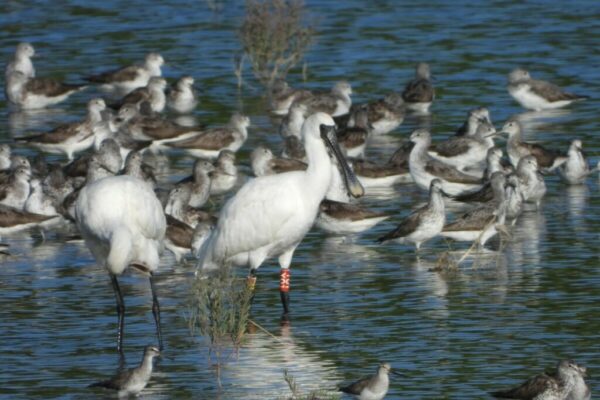
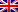
Coastal wetlands in mainland China are critically important to shorebirds. Substantial loss of tidal flats, shorebirds’ primary feeding grounds, has occurred due to coastal development. This has caused population declines in multiple species. Spartina alterniflora or “smooth cordgrass” was introduced to the coast of mainland China in 1979 to promote the conversion of tidal flats into dry land and has since spread rapidly. The occurrence of spartina reduces the availability of feeding and roosting habitat for shorebirds and may be particularly harmful in places that have experienced other tidal flat loss, for example from land claim activities.
A new article is now available which examined these issues. The article investigated how tidal flats changed between 2000 and 2015 at sites in coastal mainland China where internationally important numbers of shorebirds have been recorded, and also mapped the extent of spartina coverage in 2015 at the same sites. The authors found that:
1 – there was a 15% net loss in the tidal flat area between 2000 and 2015 across all important shorebird sites, including a net loss in the tidal flat area at 39 of 53 individual sites (74%).
2 – spartina occurred at more than half (28 of 53) of the important shorebird sites in 2015, and 22 of these sites (79%) also had a net loss in the tidal flat areas between 2000 and 2015.
3 – combined pressures from tidal flat loss and spartina invasion were most severe in eastern coastal China. Species highly dependent on migrating through this region, which include the Critically Endangered Spoon-billed Sandpiper and Endangered Nordmann’s Greenshank and Far Eastern Curlew, may be particularly impacted.
4 – experiences from around the world show that spartina control generally involves chemical treatment, and can be costly and difficult if the invasion is severe.
The authors said there is an urgent need to arrest further tidal flat declines, and to develop a comprehensive control program for spartina in coastal areas of mainland China that are important for shorebirds.
This paper is open access and available to anyone without charge at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0301479720314742
Full citation:
Jackson M.V., Fuller R.A., Gan X., Li J., Mao D., Melville D.S., Murray N.J., Wang Z., Choi C.-Y. (2021). Dual threat of tidal flat loss and invasive Spartina alterniflora endanger important shorebird habitat in coastal mainland China. Journal of Environmental Management, Volume 278, Part 2, doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111549.
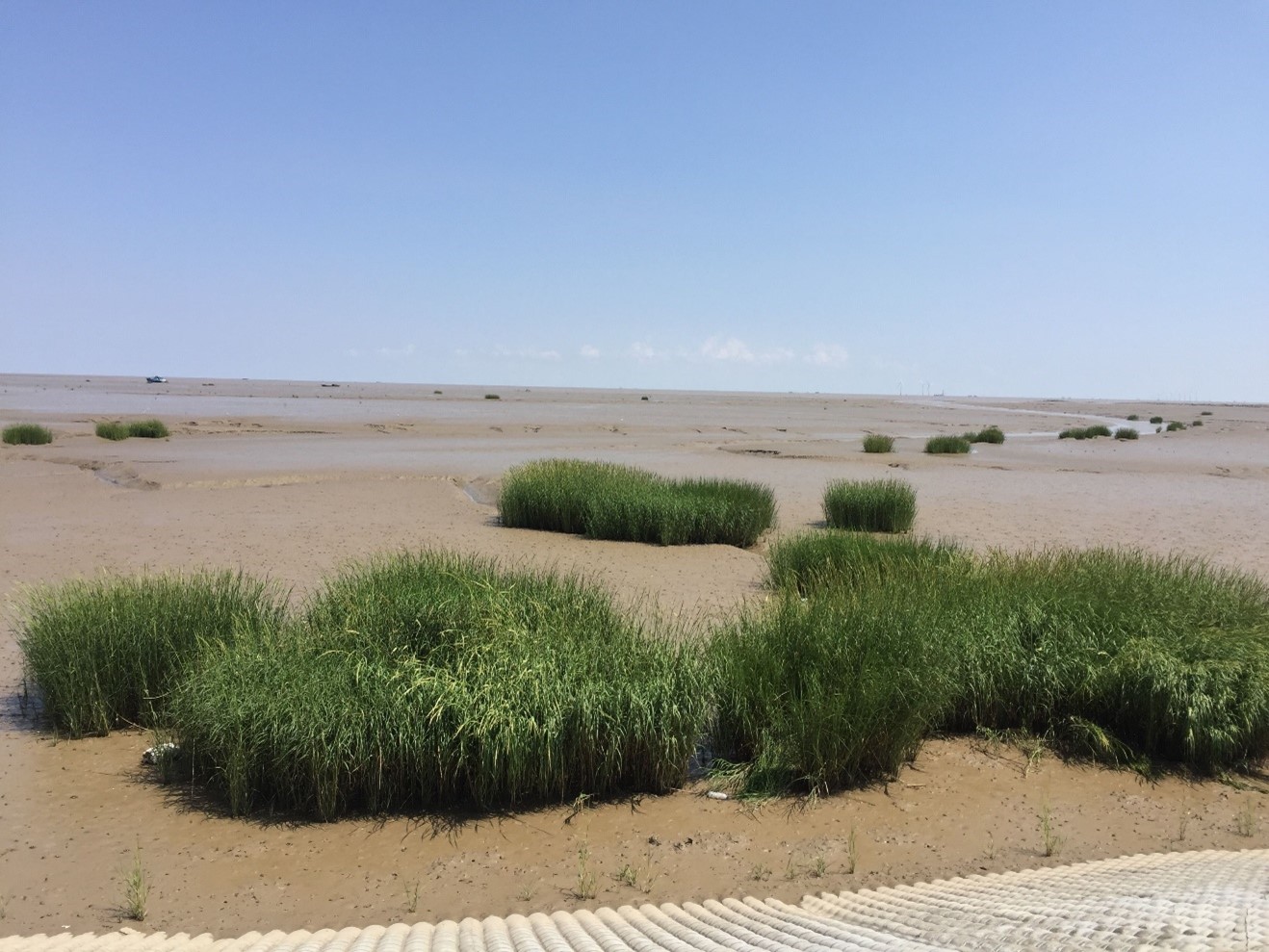

Spartina alterniflora invading tidal flats at important shorebird sites in Jiangsu province, China. © Micha V Jackson
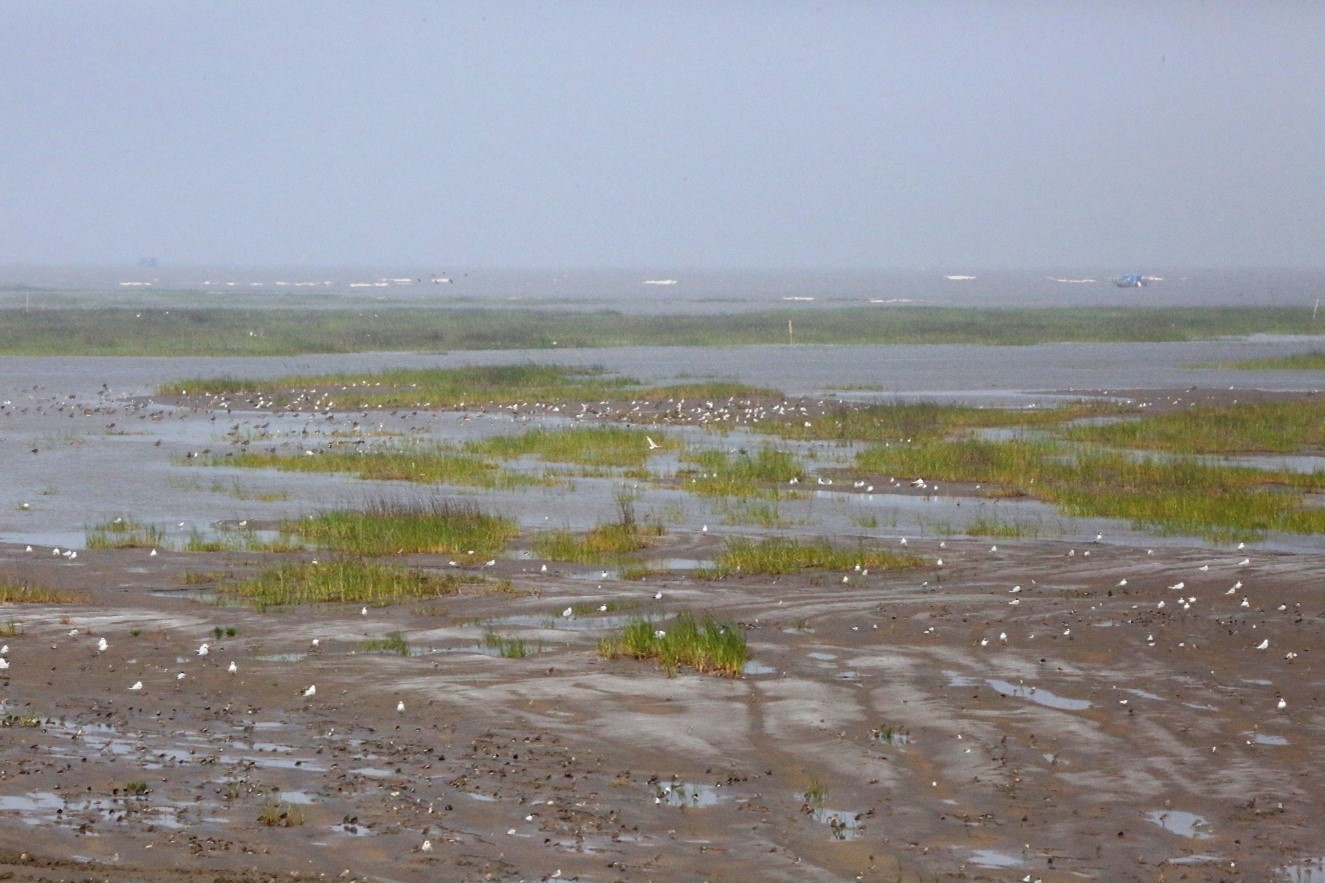

Spartina alterniflora invading tidal flats at important shorebird sites in Jiangsu province, China. © Micha V Jackson
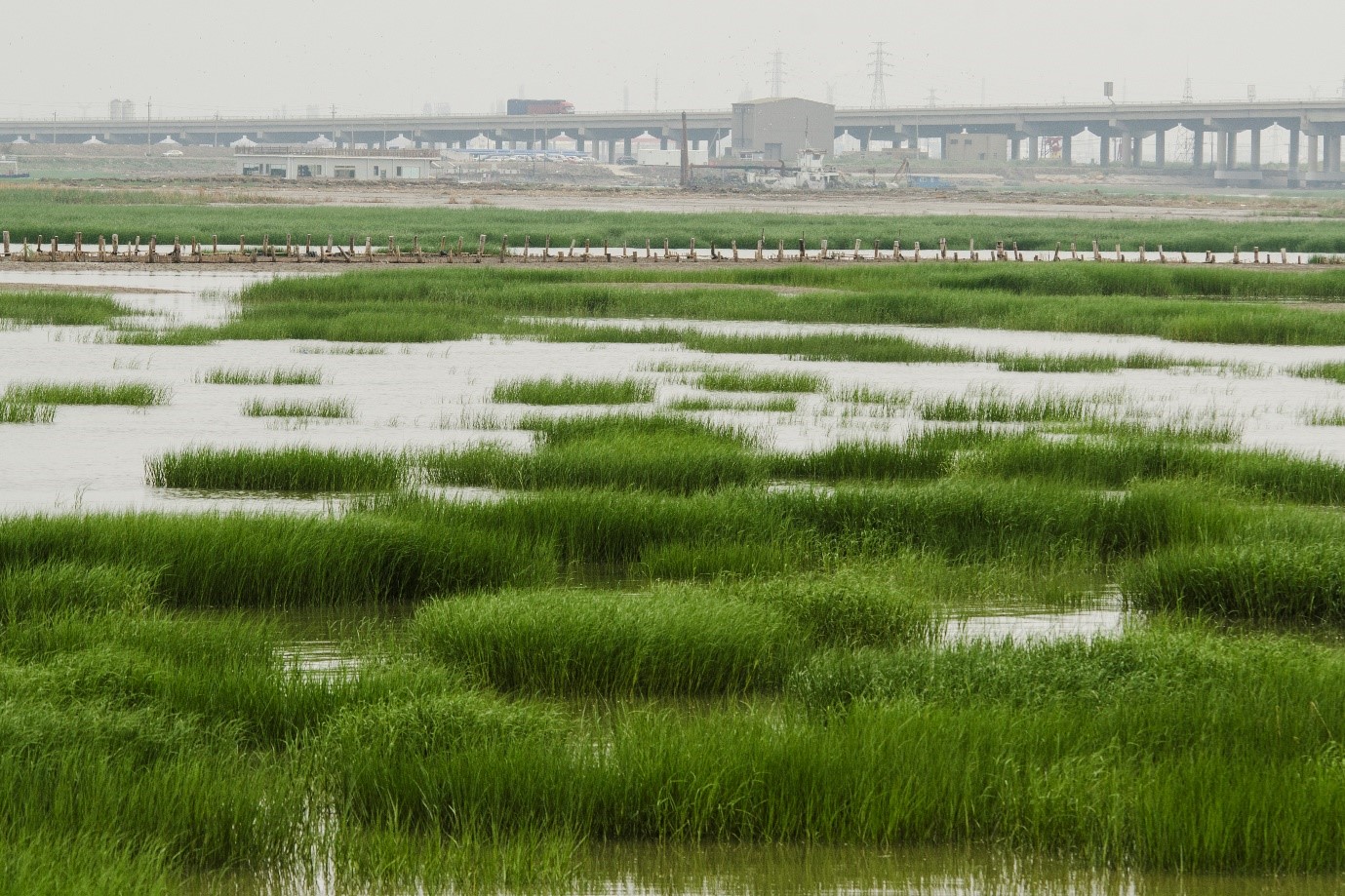

Spartina alterniflora invading in tidal flat in Tianjin © 南开小虫
Article prepared by Dr Micha V Jackson, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Centre for Biodiversity and Conservation Science, University of Queensland.
Korean ver. 국문
논문: 중국 연안의 중요한 도요물떼새류 서식지를 위태롭게 하는 침습성 갯줄풀과 (Spartina Alterniflora) 갯벌 손실.
중국 연안 습지는 도요물떼새류에게 매우 중요한 서식지다. 하지만 해안 개발로 인해 도요물떼새류의 주요 먹이터인 서식지는 상당히 유실되어 여러 종의 개체수 감소를 야기시켰다. 갯줄풀(Spartina Alterniflora)은 갯벌을 육지로 전환하기 위해 의도적으로 1979년 중국 본토 연안에 처음 도입되었으며 이후 빠르게 확산하였다. 갯줄풀의 확산은 도요물떼새류가 이용할 수 있는 먹이 및 보금자리 서식지를 감소시키며, 이미 갯벌 훼손이 진행된 다른 지역에서는 특히나 더 해로울 수 있다.
아래 소개하는 논문에서는 이러한 문제를 다루고 있다. 2000년과 2015년 사이 중국의 국제적으로 도요물떼새류 개체수가 중요하게 기록된 지역 위주로 갯벌 변화를 조사했고, 2015년에 동일한 장소의 갯줄풀 범위를 조사하여 지도에 작성하였다. 저자들은 다음과 같은 사실을 발견했다:
1 – 53개 중 39곳에서의 갯벌 순손실(74%)을 포함하여 2000년과 2015년 사이 모든 중요한 갯벌에서 15%의 순손실이 발생했다.
2 – 2015년, 주요 갯벌의 절반 이상(53곳 중 28곳)에서 갯줄풀이 발생했으며, 이 중 22곳(79%)도 2000~2015년 사이 갯벌 순손실이 있었다.
3 – 갯벌 손실과 갯줄풀 침입으로 인한 복합적인 압력으로 중국 동부 연안에서 가장 심하게 나타냈다. 이 지역 환경에 의존하는 멸종위험종 넓적부리도요와 청다리도요사촌 및 알락꼬리마도요 등 이동성 물새가 특히 영향을 받을 수 있다.
4 – 세계 각국의 사례들을 통해 갯줄풀의 통제는 일반적으로 화학적인 처리를 수반해야 하며 심할 경우 비용이 많이 들고 확산이 빠르게 진행되면 통제가 어려울 수 있다는 것을 확인했다.
저자들은 추후 갯벌 감소를 막고 도요물떼새류에게 중요한 기착지인 중국 연안 지역에 퍼진 갯줄풀를 위한 종합적 관리 프로그램 개발이 시급하다고 주장했다.
본 논문은 누구에게나 공개 접근 권한이 있으며 무료로 이용할 수 있습니다: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0301479720314742
전체 인용구: Jackson M.V., Fuller R.A., Gan X., Li J., Mao D., Melville D.S., Murray N.J., Wang Z., Choi C.-Y. (2021). Dual threat of tidal flat loss and invasive Spartina alterniflora endanger important shorebird habitat in coastal mainland China. Journal of Environmental Management, Volume 278, Part 2, doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111549.

중국 장쑤성 지역의 중요한 해안새 갯벌에 침습하는 갯줄풀. © Micha V Jackson

중국 장쑤성 지역의 중요한 해안새 갯벌에 침습하는 갯줄풀. © Micha V Jackson

톈진의 갯벌에 침습하는 갯줄풀 © 南开 小虫