– Comment from Dr. Judit Szabo, EAAFP Science Officer –
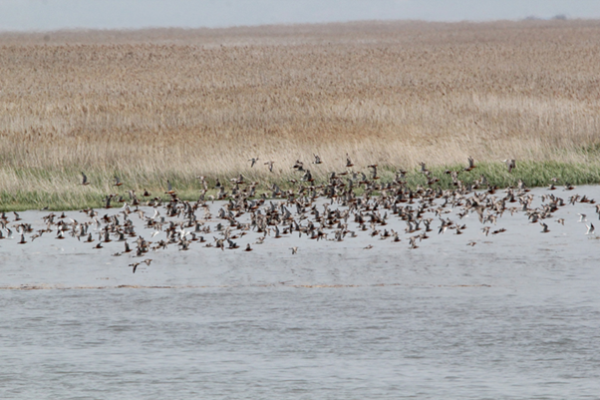
For only about one in five species of seabirds do we have reliable information of what’s going on. For these monitored species, total numbers have declined by nearly 70% in the last 60 years. The largest declines were observed in families with wide-ranging pelagic (open-sea) species, suggesting that populations that have a large range (often the whole world) may be more at risk than shorter-ranging coastal populations. This huge decline is likely caused by a suite of threatening human activities—introduced species, such as rats and cats at nesting colonies that destroy eggs and chicks, foraging adult birds getting entangled in fishing gear at sea, starvation caused by overfishing of food sources by humans, climate change and severe weather, pollution, disturbance, harvesting chicks, eggs and adults, development, and energy production. Some of these threats, such as climate change affect most species across the globe, while others are more localised.
Global trends show seabird populations dropped 70 per cent since 1950s
Media Release from The University of British Columbia
The University of British Columbia (UBC) research shows world’s monitored seabird populations have dropped 70 per cent since the 1950s, a stark indication that marine ecosystems are not doing well.
Michelle Paleczny, a UBC master’s student and researcher with the Sea Around Us project, and co-authors compiled information on more than 500 seabird populations from around the world, representing 19 per cent of the global seabird population. They found overall populations had declined by 69.6 per cent, equivalent to a loss of about 230 million birds in 60 years.
“Seabirds are particularly good indicators of the health of marine ecosystems,” said Paleczny. ”When we see this magnitude of seabird decline, we can see there is something wrong with marine ecosystems. It gives us an idea of the overall impact we’re having.”
The dramatic decline is caused by a variety of factors including overfishing of the fish seabirds rely on for food, birds getting tangled in fishing gear, plastic and oil pollution, introduction of non-native predators to seabird colonies, destruction and changes to seabird habitat, and environmental and ecological changes caused by climate change.
Seabirds tend to travel the world’s oceans foraging for food over their long lifetimes, and return to the same colonies to breed. Colony population numbers provide information to scientists about the health of the oceans the birds call home.
Albatross, an iconic marine bird that lives for several decades, were part of the study and showed substantial declines. Paleczny says these birds live so long and range so far that they encounter many dangers in their travels. A major threat to albatross is getting caught on longline fishing hooks and drowning, a problem that kills hundreds of thousands of seabirds every year.
“Our work demonstrates the strong need for increased seabird conservation effort internationally,” said Paleczny. “Loss of seabirds causes a variety of impacts in coastal and marine ecosystems.”
Seabirds play an important role in those ecosystems. They eat and are eaten by a variety of other marine species. They also transport nutrients in their waste back to the coastal ecosystems in which they breed, helping to fertilize entire food webs.
The study, published in PLOS ONE, is the first to estimate overall change in available global seabird population data. It is a collaboration between UBC researchers Paleczny, Vasiliki Karpouzi and Daniel Pauly and Edd Hammill, a lecturer at the University of Technology, Sydney in Australia.
Find other stories about: Michelle Paleczny, Sea Around Us, Seabirds
The original article: Click HERE
Relevant articles:
- Seabirds and fishing gear – a conundrum
- Great news for Pacific seabirds and marine mammals as Russia bans driftnet fishery
Scientific articles about seabirds: Click HERE